[Paper Review] DDPM: Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models 논문 리뷰
업데이트:
- Paper: Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (Arxiv 2020): arxiv, code, project page
Diffusion Probabilistic Models
- data에 임의의 noise를 더해준 후(forward process), noise를 제거하는 과정(reverse process)을 학습하는 모델
- forward process (diffusion process): data에 noise를 추가하는 과정으로, markov chain을 통해 점진적으로 noise를 더해나간다.
- reverse process: gaussian noise에서 시작하여 점진적으로 noise를 제거해가는 과정
1. DPM
- Paper: Deep Unsupervised Learning using Nonequilibrium Thermodynamics (2015): arxiv
딥러닝에서 현실의 복잡한 dataset을 확률분포 probability distribution로 표현하는 것은 매우 중요하다. 특히 우리가 이 확률분포를 구하고자 할 때에는 tractability와 flexibility라는 개념이 중요한데, 이는 서로 trade-off 관계에 있기 때문에 이 둘을 동시에 만족하긴 어렵다. (복잡한 data에 대해서도 잘 fitting이 되어 있으면서도 계산이 용이한 분포를 찾긴 어려움)
- tractability: Gaussian이나 Laplace distribution 처럼 data에 쉽게 fitting되어 분석이 쉬우며 계산이 용이한 분포
- flexibility: 임의의 복잡한 data에 대해서도 적용이 가능한 분포
Diffusion Probability Model
- extreme flexibility in model structure
- exact sampling
- easy multiplication with other distributions, e.g. in order to compute a posterior, and
- the model log likelihood, and the probability of individual states, to be cheaply evaluate
초창기 Diffusion Probability Model(2015)에서는 diffusion 과정을 통해 우리가 잘 알고있는 distribution (ex. Gaussian)을 target data distribution으로 변환해주는 markov chain을 학습시켜 flexible하면서도 tractable한 distribution을 구하고자 하였다.
2. Diffusion Model
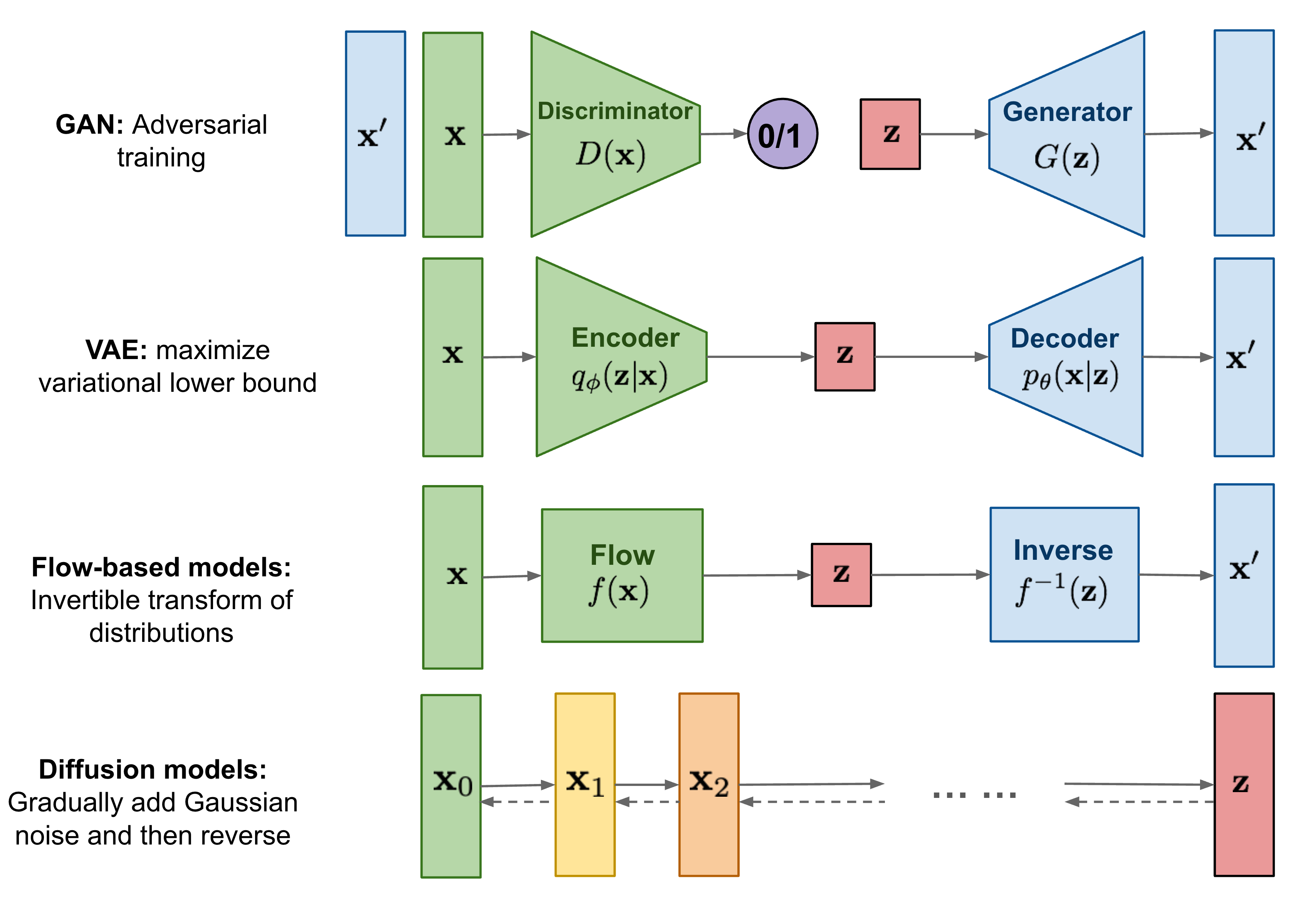
출처: https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2021-07-11-diffusion-models/
VAE는 image를 encoding하는 network와 latent code를 바탕으로 image를 decoding하는 network 모두를 학습하는 반면, Diffusion model은 이미지를 encoding하는 forward process는 fix된 채 image를 decoding하는 reverse process - single network 만을 학습한다.
2.1 Forward Process (diffusion process)
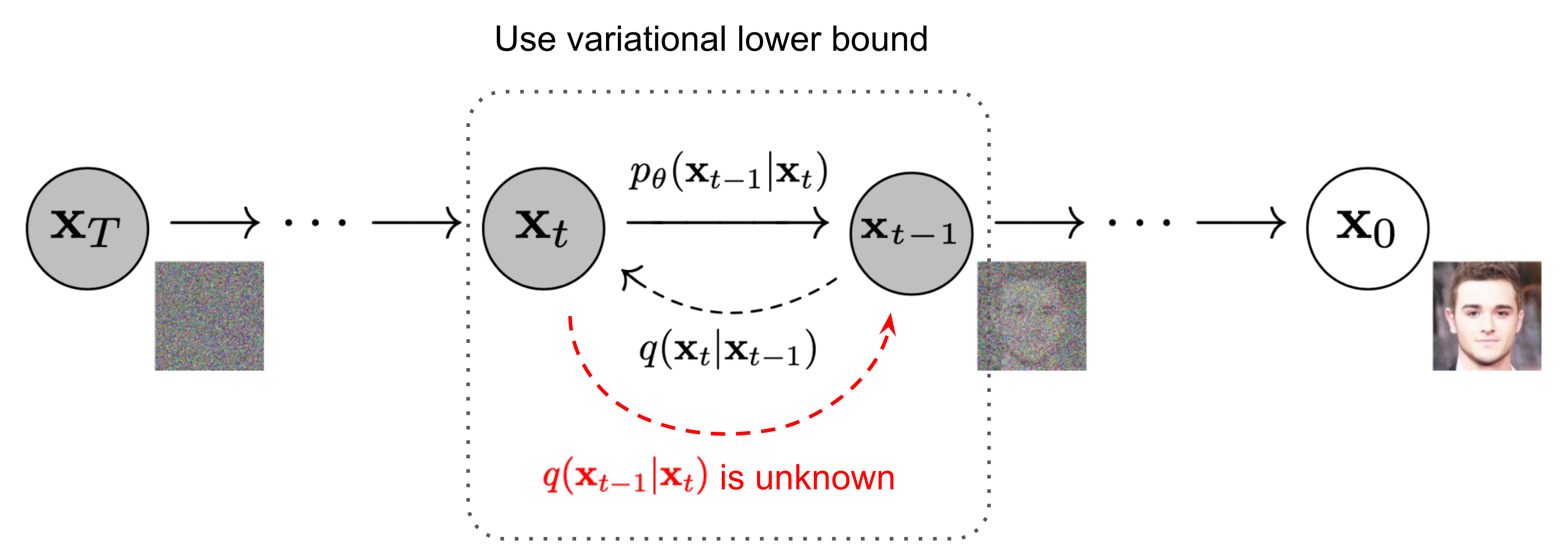
- markov chain으로 data에 점진적으로 noise를 추가하는 과정이다 (sampling의 반대방향)
- data에 noise를 추가할 때, variance schedule
를 이용하여 scaling을 한 후 더해준다.
- 매 step마다 gaussian distribution에서 reparameterize를 통해 sample하게 되는 형태로 noise는 추가되는데, 이때 단순히 noise만을 더해주는게 아니라
로 scaling하는 이유는 variance가 발산하는 것을 막기 위함이다.
- variance를 unit하게 가둠으로써 forward-reverse 과정에서 variance가 일정수준으로 유지될 수 있게 된다
- 이 값은 learnable parameter로 둘 수도 있지만, 실험을 해보니 상수로 두어도 큰 차이가 없어서 constant로 두었다고 한다.
- 데이터가 이미지와 비슷할 때에는 이 값을 매우 작게 설정하다가 gaussian distribution에 점점 가까워질 수록 이 값을 크게 설정 (10^-4에서 0.02로 linear하게 증가)
- 매 step마다 gaussian distribution에서 reparameterize를 통해 sample하게 되는 형태로 noise는 추가되는데, 이때 단순히 noise만을 더해주는게 아니라
- t번의 sampling을 통해 매 step을 차근차근 밟아가면서
에서
를 만들 수도 있지만, 한번에 이를 할수도 있다.
- 재귀적으로 식을 정리하다보면, 다음과 같은 식이 성립
- 한 step씩 학습을 하면 메모리와 resource가 너무 많이 든다. 그러나 이런식으로 한번에
를 만들고 나면, 여기서 loss를 구한 다음에 t에 대한 expectation을 구하는 식으로 학습이 가능하다 (어차피 stochastic gradient를 사용하기 때문에 이런식으로 학습해도 무방)
- 증명

2.2 Reverse Process
- 우리가 학습하고자 하는
reverse diffusion과정- Hierarachical VAE에서의 decoding과정과 비슷
- Gaussian noise
에서 denoising 하면서 이미지
를 만드는 과정
2.3 정리
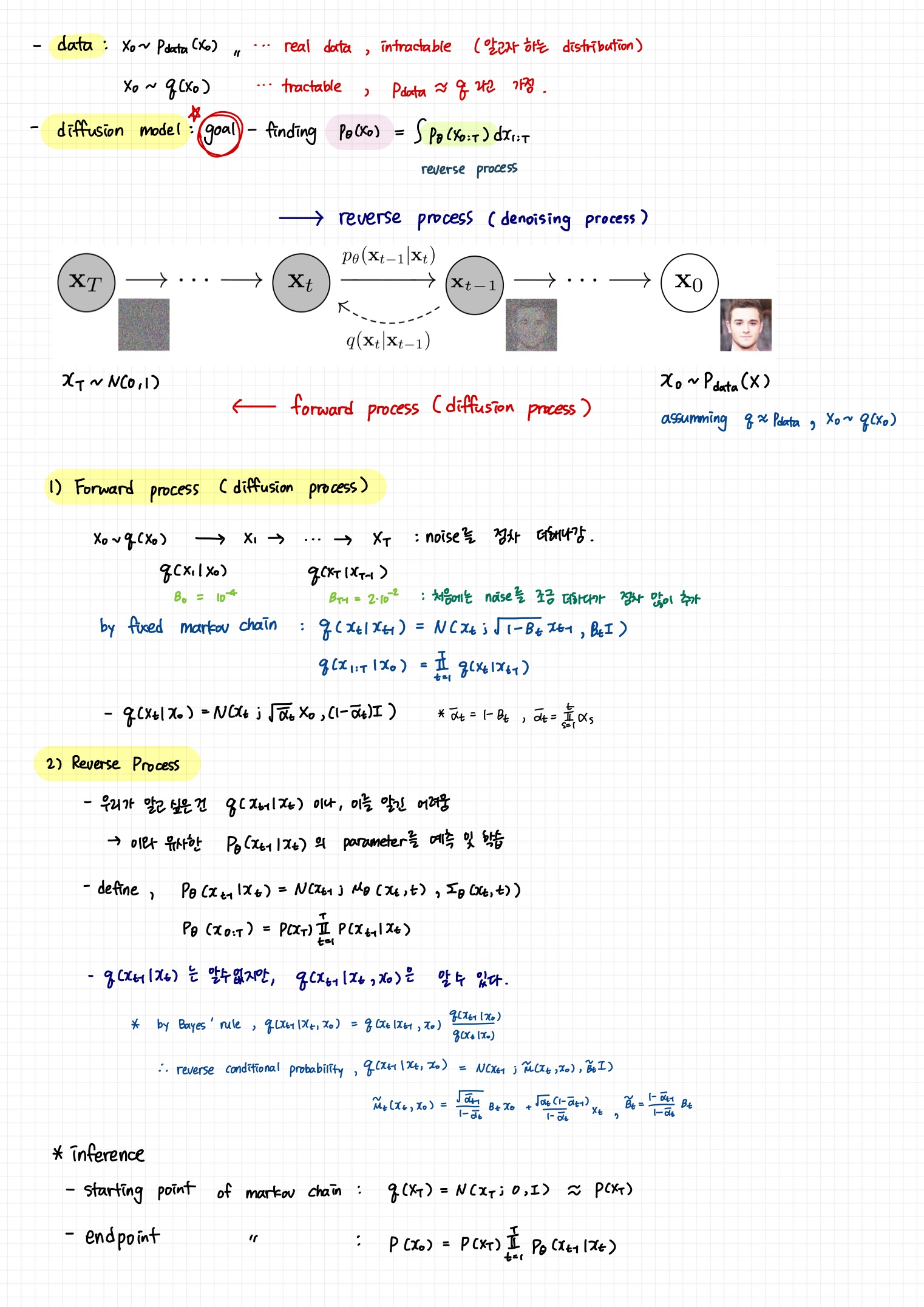
3. Diffusion models and denoising autoencoders
3.1 Objective Function

여기서 가장 중요한 term은 이다. 우리는
부터 시작하여 conditional하게 식을 전개하다보면,
tractable한 forward process posterior
의 정규분포를 알 수 있는데,
이를 바탕으로 KL divergence를 계산하면 우리가 결과적으로 학습하고자하는
를 학습시킬 수 있다.
3.2 Forward process and 

- 위 objective function의 첫번째 term
- DDPM에서의 forward process는
가 항상 gaussian distribution을 따르도록 하기 때문에 사실 상 tractable한 distribution,
는 prior
와 거의 유사하다. 또한, DDPM에서는 forward process variance
를 constant로 고정시킨 후 approximate posterior를 정의하기 때문에 이 posterior
에는 learnable parameter가 없다.
- 따라서 이 loss term은 항상 0에 가까운 상수이며, 학습과정에서 무시된다.
3.3 Reverse process and 

- 위 objective function의 두번째 term
-
이 loss term에서는
(1)
을 예측하도록
the reverse process mean function approximator,를 훈련시켜도 되고
(2)
을 예측하도록 학습해도 되는데, 저자들은
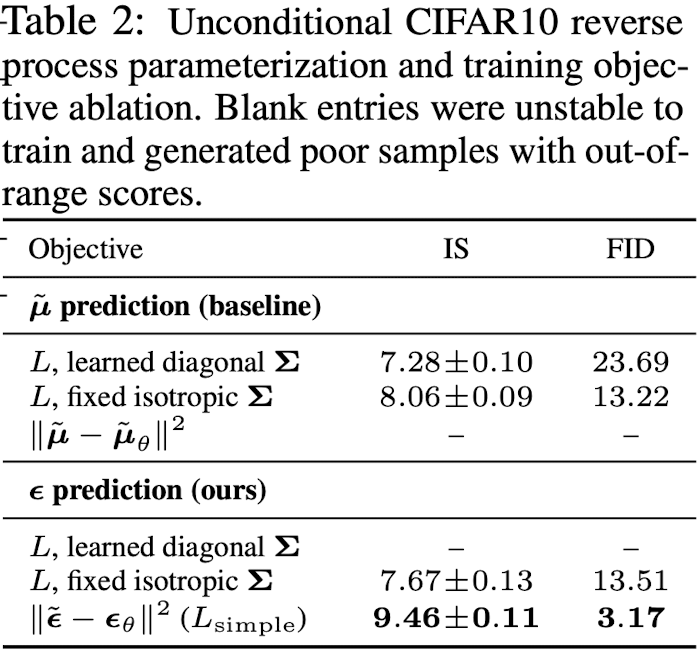
을 예측하도록 loss term을 simplification하는게 성능이 좋다고 말하고 있음 (
ablation study, Table 2)- fixed variances를 사용하는게 더 성능이 좋음
3.4 Data scaling, reverse process decoder, and 
3.5 Simplified training objective
위 objective function에서 중요한 term은 variational bound에 해당하는 과
이다. 저자들은 해당 loss term 을 아래와 같이 simplification 했다고 한다.
- t is uniform between 1 and T
- 위와 같은 simplified objective을 통해 diffusion process를 학습하면 매우 작은 t 에서뿐만 아니라 큰 t에 대해서도 network 학습이 가능하기 때문에 매우 효과적
3.6 Training & Sampling

- Algorithm 1: Training
- noise를 더해나가는 과정, network(
,
)가 t step에서 noise(
)가 얼마만큼 더해졌는지를 학습한다.
-
학습 시에는 특정 step의 이미지가 gaussian noise에서 얼마나 denoising 되었는지를 예측하도록 학습된다.
- noise를 더해나가는 과정, network(
- Algorithm 2: Sampling
- network를 학습하고 나면, gaussian noise에서 시작해서 순차적으로 denoising 하는 것이 가능하다. (by parameterized markovian chain)
4. Experiments

4.1 Sample quality

댓글남기기