About Talking Head Models #01: Definition, Methods, SoTA Models, Warping based model…
업데이트:

Talking Head Task Example [출처](https://gfycat.com/ko/horribledampislandcanary-generative-adversarial-networks)
Neural Talking Head Model 이란?
Talking Head Model는 적은 수의 이미지를 가지고 특정 video의 표정이나 움직임을 따라하게 해주는 모델이다.
이때, reference가 되는 비디오를 driving video라고 부르며, target video(talking head model로 만들고 싶은 결과 비디오)의 identity를 가지고 있는 이미지를 source image라고 부른다.
Talking Head Model은 크게 세가지의 방식을 따른다.
- Warping based model
- pixel을 움직여 이미지를 조작하는 방식
- Warping based의 talking head model은 적은 수의 이미지(few-shot images)로 talking head video를 생성할 수 있으나, 다양한 동작이나 움직임 등을 합성하긴 어려움
- Direct synthesis (warping-free)
- Deep Conv Network를 adversarial하게 학습하는 모델
- large dataset으로 large network를 훈련시켜야하기 때문에 학습이 오래 걸리며 많은 GPU가 필요
- Meta Learning
- large talking-head datasets(ex.
VoxCeleb)으로 deep ConvNet을 학습 시킨 후, few-shot의 이미지를 가지고 meta-learning을 하여 원하는 새로운 사람(target person)에 대해 talking head video를 만드는 방식 - Meta Learning 이란?
- Meta-Learning은 “learn to learn”이라고도 불리는데, 한마디로 학습하는 법 자체를 배운다는 뜻이다. meta-learning에서는 모델이 새로운 task/data를 빠르고 잘 학습하는 것을 목표로 한다.
- meta-learning은 meta-training과 meta-testing 단계로 학습된다. meta-training에서 large data에 대해 학습을 한 후, meta-testing에서 새로운 data나 task에 잘 적용이 되도록 짧게 학습을 한다.
- meta-testing에서 좋은 성능을 얻으려면 meta-training 과정에서 다음의 조건을 만족하도록 학습을 해야한다.
- meta-testing에서 조금만 update를 해도 되도록 좋은 parameter를 찾는 것
- 새로운 data와 task에 대해서도 학습이 잘 되도록 generalization을 잘 해놓는 것
- large talking-head datasets(ex.
Talking Head Talk는 사람의 표정뿐만 아니라 주위의 배경, head rotation 등을 반영한 자연스러운 비디오를 생성해야하기 때문에 매우 어렵다. Talking Head model은 target이 되는 사람의 움직임을 조절하기 위해 audio, landmark등을 이용한다.
- Graphics-based talking head generation
- subject-dependent하게 video를 editing하는 방식. input으로 특정 사람에 대한 full-original video가 필요하다.
Synthesizing Obama: Learning Lip Sync from Audio (SIGGRAPH 2017) : Paper- audio signal을 input으로 받아서 lip region을 합성. target person에 대한 large video corpus가 필요
TETH: Text-based Editing of Talking-head Video (SIGGRAPH 2019) : Paper
- Audio-driven face generation (fixed head pose)
- head가 고정된 상태에서 identity-independent하게 표정을 변화시키는 face generation 방식
- Landmark-driven talking head generation
- facial landmark로 target person의 facial expression과 head rotation을 조절하는 방식
FSTH: Few-Shot Adversarial Learning of Realistic Neural Talking Head Models (arxiv 2019) : PaperLPD: Neural Head Reenactment with Latent Pose Descriptors (IEEE 2020) : Paper
Various Talking Head Model
본 포스팅에서는 Talking Head Model들 중에서 Warping based model에 대해 살펴볼 예정이다.
Talking Head model Paper 모음집은 이 링크에 🤗
X2Face: A network for controlling face generation by using images, audio, and pose codes (ECCV 2018) : Paper, projectMonkey-Net: Animating Arbitrary Objects via Deep Motion Transfer (CVPR 2019) : Paper, project, codeFOMM: First Order Motion Model for Image Animation (NeurIPS 2019) : arxiv, codeface vid2vid: One-Shot Free-View Neural Talking-Head Synthesis for Video Conferencing (CVPR 2021): arxiv, project- Motion Representations for Articulated Animation (CVPR 2021) : arxiv, code, project
MocoGAN-HD: A Good Image Generator Is What You Need for High-Resolution Video Synthesis (ICLR 2021) : arxiv, code, project
X2Face: A network for controlling face generation by using images, audio, and pose codes (ECCV 2018)
⭐️ Keyword: Warping based model, self-supervised training
X2Face: A network for controlling face generation by using images, audio, and pose codes (ECCV 2018) : arxiv, project

First training-stage: fully self-supervised

Second training-stage
Model
- Embedding network : source frame으로부터 identity를 뽑아내는 network
- U-Net 과 pix2pix 의 architecture를 따름
- 이 네트워크는 source frame의 정면화된 얼굴을 추출하라고 강요하지는 않지만, pose/표정과 무관한 source frame만의 고유한 얼굴을 생성하려고 하다보니 embedded face가 정면을 바라보는 얼굴로 생성됨
- Driving network
- encoder-decoder architecture
- driving frame(input)으로 부터 driving vector를 embedding한 후(latent embedding), embedded face를 pixel단위로 transform하여 target image 생성
Training
- Training the network : 총 2 stages로 training 함
- First training-stage: fully self-supervised
- ex) 같은 비디오에서 4개의 프레임을 추출했을 때, 3개는 source image로 사용하고, 나머지 하나의 프레임은 driving frame으로 사용. source frame으로부터 얻은 embedded face와 driving frame에서 얻은 driving vector를 이용하여 이미지를 생성한 후, 생성된 이미지와 driving frame간에
L1 loss를 통해 network를 업데이트 - 이렇게만 학습을 하면 생성된 이미지가 embedded face에서 identity에 대한 정보를 얻지 않고, driving vector에서도 identity에 대한 정보를 얻을 수 있음. second training-stage에서 identity loss function을 도입하여 identity bleeding이 생기지 않도록 함
- ex) 같은 비디오에서 4개의 프레임을 추출했을 때, 3개는 source image로 사용하고, 나머지 하나의 프레임은 driving frame으로 사용. source frame으로부터 얻은 embedded face와 driving frame에서 얻은 driving vector를 이용하여 이미지를 생성한 후, 생성된 이미지와 driving frame간에
- Second training-stage
- Generated frame이 source frame의 identity를 따르도록 강제하는 identity loss function을 둠
- $L_{identity}$는 사전에 훈련된 11-layer VGG network를 사용
- 두가지의 loss term
- $L_{identity}(d_A, g_{d_A})$: $g_{d_A}$와 $d_A$는 pose, 표정, identity 등 모든게 같음(사실상 recon loss). photometric L1 loss와 L1 content loss를 사용
- $L_{identity}(s_A, g_{d_R})$: L1 content loss만을 사용
- First training-stage: fully self-supervised
- Result

- Comparison

Monkey-Net: Animation Arbitrary Objects via Deep Motion Transfer (CVPR 2019)

⭐️ Keyword: MOviNg KEYpoints, Warping based model, optical flow, self-supervised training, object-agnostic deep model
Model

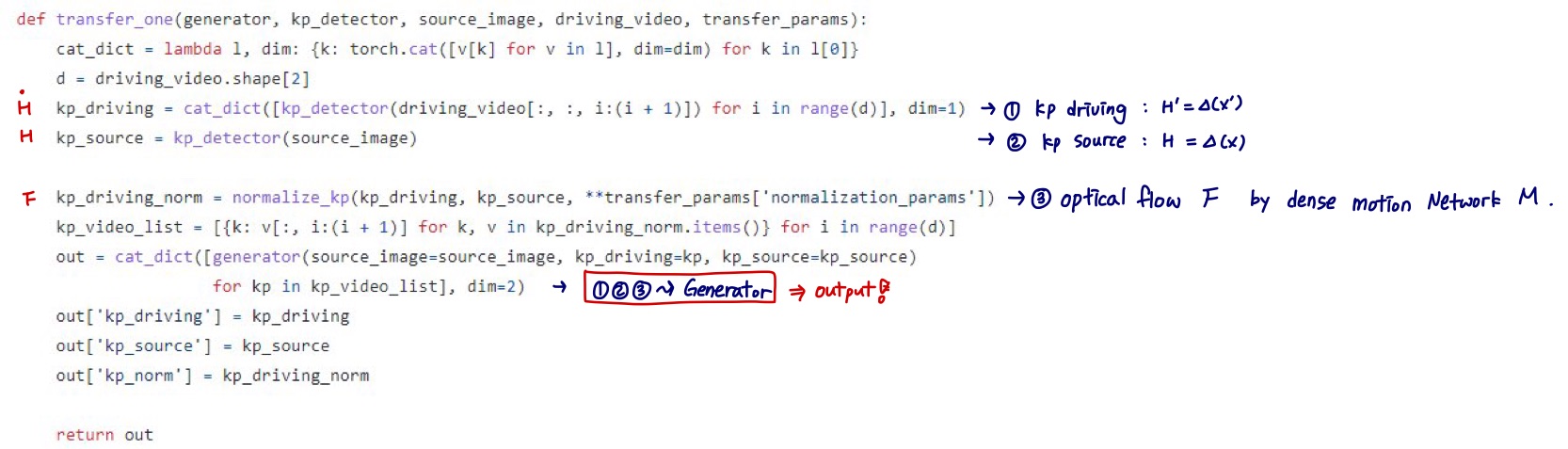
(1) Keypoint Detector $\triangle$
- 물체의 keypoint를 추출할 수 있도록 unsupervised 하게 학습
- source image와 driving video의 frame들로부터 sparse keypoint를 추출함 (object의 structure 뿐만 아니라 motion까지 capture)

(2) Dense Motion prediction network
- sparse keypoint에서 dense motion heatmap을 생성해서 motion 정보를 더 잘 encoding 할 수 있게 함

(3) Motion Transfer Generator Network $G$
- dense motion heatmap과 외형에 대한 정보를 이용하여 output frame을 합성
- convolutional block으로 된 encoder-decoder 구조

(4) Final
Training
- X2face처럼 self-supervised 방식으로 object의 latent representation을 학습
- Loss Function : GAN Loss + Feature-matching Loss
- GAN Loss
- real image $\boldsymbol{x}^{\prime}$, generated image $\hat{\boldsymbol{x}^{\prime}}$
- Discriminator Loss: real image $\boldsymbol{x}^{\prime}$ 를 1로 판별하려고 하고, fake image $\hat{\boldsymbol{x}^{\prime}}$ 를 0으로 판별하려고 함
- Generator Loss: fake image $\hat{\boldsymbol{x}^{\prime}}$ 가 real(1) 처럼 보이게
Discriminator를 속이려고 함
- Feature-matching Loss
- VGG pretrained model이 필요한 perceptual loss와 다르게 이 loss는 external pretrained network가 필요 없음
Inference (Test) Time
-
source image는 driving video에서 뽑은 keypoint trajectory에 따라 움직이게 됨
-
Result

FOMM: First Order Motion Model for Image Animation (NeurIPS 2019)

⭐️ Keyword: Monkey-Net의 후속 논문, Warping based model, optical flow, self-supervised training, local affine transformation, occlusion-masking

Monkey-net: driving이 생긴 부분이 이상하게 그려짐
- Monkey-Net의 후속 논문 ✨ (같은 1저자!)
- Monkey-net은 heatmap을 바탕으로 이미지를 warping할 때, keypoint 주변의 object appearance를 제대로 변환하지 못함 (위의 그림 참고, 저자들은 Monkey-Net을 0-th model라고 부름) ➡ First-Order Model에서는
local affine transformation과occlusion-aware generator를 도입하여 이를 해결 - X2face, Monkey-Net와 마찬가지로 self-supervised 방식으로 학습
- Monkey-net은 heatmap을 바탕으로 이미지를 warping할 때, keypoint 주변의 object appearance를 제대로 변환하지 못함 (위의 그림 참고, 저자들은 Monkey-Net을 0-th model라고 부름) ➡ First-Order Model에서는
Model
✍🏻 First-Order Model은 Monkey-Net의 후속 논문으로, 사실상 구조가 비슷하다. 차이점은 (1) self-learned keypoint를 뽑을 때 local affine transformation을 하여 모델의 motion을 보다 더 정교하게 뽑는 다는 것과 (2) occlusion-aware generator: 이미지의 context를 파악하도록 도와주는 occlusion mask를 사용한다는 점이 있다.

(1) Motion Estimation Module
- Goal ⭐: dense motion field 예측 - $S$ 로부터 feature map을 계산해서 $D$ 의 object pose로 align
Unsupervised keypoint detector와Dense Motion network로 구성- self-supervised 방식으로 학습된
keypoint detector로 부터 keypoint를 뽑은 후,local affine transformation으로 각 keypoint 주변의 motion들을 modeling- 단순히 keypoint displacement 만을 사용하는 것보다
local affine transformation을 하면 더 큰 범위에 대해 transformation을 할 수 있음 (affine 변환 자체가 이 논문의 contribution ✨)
- 단순히 keypoint displacement 만을 사용하는 것보다
(1-1) Local Affine Trnasformations for Approximate Motion Description
- forward optical flow 방식이 아닌 backward optical flow 방식을 채택
- FOMM에서는 다소 특이한 방식으로 이미지를 생성한다. source image를 driving video의 pose로 transform 시킬 때, source image를 바로 변형시키지 않고 중간에 abstract reference frame $R$ 을 사용하여 변형시킨다. 이렇게 하면 $D$와 $S$를 독립적인 방식으로 processing할 수 있다.
- 수식 설명

(1-2) Combining Local Motion
- $\hat{\mathcal{T}}_{\mathbf{S}\leftarrow \mathbf{D}}$ 는 $D$ 의 pixel location에 mapping되어 있으므로 $S$ 와 pixel-to-pixel로 align을 할 필요가 있음 (edge, texture…) ➡ Source frame $S$ 를 feature warping strategy에 따라 transform !
- Dense motion network로 heatmap $\mathcal{H}_k$ 계산
- Monkey-net 처럼 optical flow를 masking
(2) Occlusion-aware Image Generation

Training
- Reconstruction Loss: Monkey-net과 다르게 feature matching loss가 아닌 VGG-19 network로 pretrain 된
perceptual loss를 사용- MS-SSIM과 비슷하게 resolution 별로 이 loss를 사용
- Result



face vid2vid: One-Shot Free-View Neural Talking-Head Synthesis for Video Conferencing (CVPR 2021)
⭐️ Keyword: NVIDA, Warping based model, optical flow, self-supervised training
face vid2vid: One-Shot Free-View Neural Talking-Head Synthesis for Video Conferencing (CVPR 2021): arxiv, project


댓글남기기