[Paper Review] Pix2pix : Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks 논문 분석
업데이트:
✍🏻 이번 포스팅에서는 image to image의 초창기 모델로 유명한 Pix2Pix model에 대해 살펴본다.
2021.04.13 기준으로 8621회 인용되었네요…😮
- Paper : Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks (CVPR 2017 / Phillip Isola, Jun-Yan Zhu, Tinghui Zhou, Alexei A. Efros)
- Image-to-Image Demo
-
Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Nets Site
- GAN-Zoos! (GAN 포스팅 모음집)
⭐Pix2pix : Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks
Key Point
- input에서 output image로 mapping하는 Conditional Adversarial Networks
- mapping network 훈련에 사용되는 loss function
paired dataset에 대해 image-to-image task를 수행한다.
1. Introduction
기존에는 CNN을 이용하여 image-to-image task를 수행하려는 노력이 많았었다.
다만, CNN은 loss 값을 최소화하도록 최적화된 network이기 때문에 loss function을 잘 디자인해야 좋은 performance를 낸다는 단점이 있다. 또한, CNN은 predicted와 ground truth의 pixel들간의 Euclidean distance를 최소화하도록 훈련이 되는데 이 경우에는 blurry한 결과가 생긴다는 단점이 있다.
⭐ General-purposed image to image translation framework
따라서 진짜와 같은 이미지를 만드려면 목적에 맞게 loss function을 자동적으로 배우는 network가 필요했고 본 논문에서는 이를 위해 GAN을 사용하였다. conditional GAN은 image-to-image translation에 적합하며 특정 application이 아니라 전반적인 image-to-image 분야에 적용할 수 있다.
2. Related work
2.1 Structured losses for image modeling
기존에는 image-to-image task에 per-pixel classification이나 regression등이 사용되었다. 이 경우에는 output space가 unstructed되어 있어 각 output pixel들이 input 이미지에 독립적인 것처럼 다뤄졌다. cGAN에서는 structed loss를 사용한다.
2.2 Conditional GANs
지난 연구들은 image-to-image에 GAN을 unconditional하게 적용하였다면, pix2pix에서는 Conditional GAN을 사용한다.
3. Method
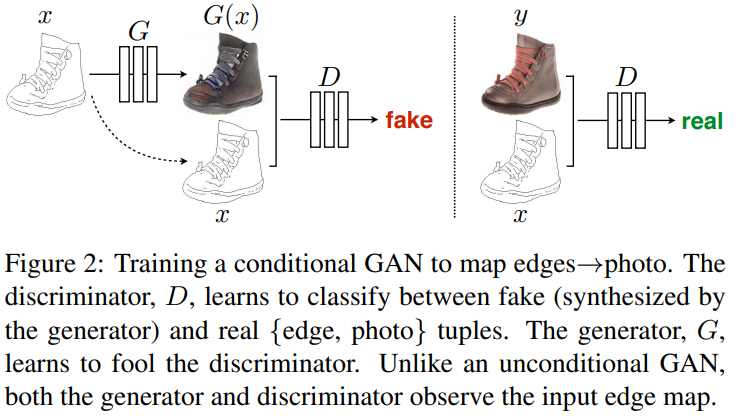
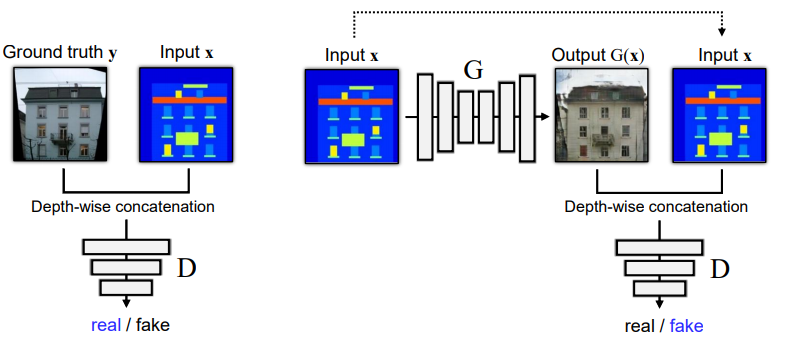
⭐ Pix2pix에서는 Generator로는 U-Net 구조를, Discriminator로는 PatchGAN을 사용한다.
cGAN의 Generator에서는 위 그림과 같이 real image $x$와 random noise vector $z$에서 이미지를 생성한다. \(G:\{x, z\} \rightarrow y\)
3.1 Objective
cGAN Loss
object function으로는 conditional GAN을 사용하여 input image와 output image가 잘 matching되는지도 학습 하도록 하였다. (unconditional도 실험을 해봤지만, cGAN의 성능이 더 좋았음)
\[\begin{aligned} \mathcal{L}_{c G A N}(G, D)=& \mathbb{E}_{x, y}[\log D(x, y)]+\mathbb{E}_{x, z}[\log (1-D(x, G(x, z))] \end{aligned}\]L1 Loss
또한, pix2pix는 추가적인 loss term을 추가한다. cGAN loss를 사용하면 G가 D를 잘 속이도록 학습이 되지만, G는 D를 속이는 것만이 목적이기 때문에 ground truth output과 생성된 이미지가 달라질 수도 있다.
따라서 생성된 이미지와 대응되는 진짜 이미지와의 거리를 loss에 추가하여 생성된 이미지가 진짜 이미지와 비슷할 수 있도록 학습하였다. (이때, 논문에서는 L2보다 L1을 사용했을 때 blurring 현상이 더 줄었다고 한다.)
\[\mathcal{L}_{L 1}(G)=\mathbb{E}_{x, y, z}\left[\|y-G(x, z)\|_{1}\right]\]Final Loss Function
\[G^{*}=\arg \min _{G} \max _{D} \mathcal{L}_{c G A N}(G, D)+\lambda \mathcal{L}_{L 1}(G)\]-
pix2pix의 문제
z가 없다면x에서 deterministic한 outputy이 생성될 수 있으므로 noise z를 꼭 추가해야한다.- 실험 결과
G가 noizez를 무시하고 학습을 한다.(noise를 무시하고 학습하는 게 훨씬 안정적)- noise를 사용하도록 dropout의 방식도 사용해봤지만, 여전히 stochastic한 변화는 미미했다.
- 따라서 본 논문에서는 noise
z를 빼고 실험하였다.(있으나 마나여서) - Generator가 학습시에 noise를 무시하여 생기는 문제는 향후 bicycleGAN에서 개선된다.
- 실험 결과
3.2 Network architectures
Convolution-BatchNorm-ReLU
본 논문에서는 DCGAN의 G와 D를 baseline으로 사용하였다.
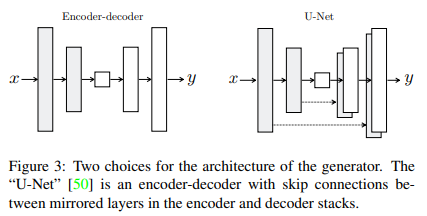
3.2.1 Generator with skips(U-Net)
image-to-image translation에서는 high resolution input grid를 high resolution output grid로 mapping하는 것이 중요하다. input과 output의 구체적인 특징은 다르지만, 전반적인 structure는 동일할 것이다.
Generator의 기본적인 architecture는 Encoder-Decoder에 skip connection을 추가한 U-Net을 따른다.
- Encoder-Decoder : bottleneck까지 input을 downsampling을 한 후, decoder에서는 다시 upsampling을 한다.
- Encoder의 정보가 Decoder까지 전달이 안되는 것을 막기 위해 skip-connectoin기법을 추가한다.
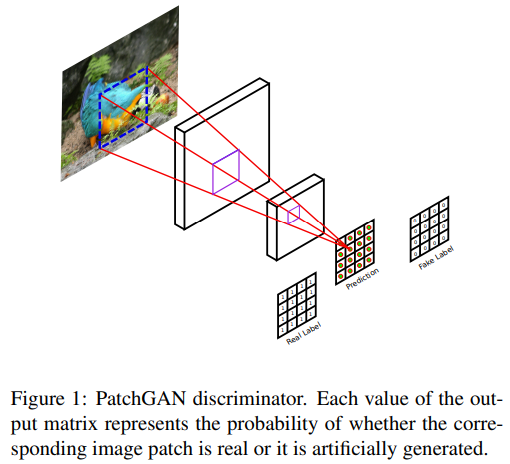
3.2.2 Markovian discriminator (PatchGAN)
L1 loss는 low-frequency에서 진짜 이미지와 비슷한 이미지를 생성하도록 돕지만, high-frequency에 대해서는 진짜와 비슷한 이미지를 생성하도록 해주지는 못한다. 따라서 high-frequency structure를 modeling하기 위해 discriminator를 사용한다.
discriminator의 architecture로는 PatchGAN을 사용한다.
- PatchGAN은 Precomputed Real-Time Texture Synthesis with Markovian Generative Adversarial Networks (2016)논문에서 처음으로 제시된 모델이다.
- 사진은 Patch-Based Image Inpainting with Generative Adversarial Networks (2018) 논문의 PatchGAN discriminator
D는 이미지의 N x N의 patch(high frequency 영역)가 진짜인지 가짜인지를 판별한다. 이 방식은 discriminator를 좀더 약하게 만들어준다고도 볼 수 있다. (D를 약하게 함으로써 학습을 안정화)
3.3 Optimization and inference
- minibatch SGD와 Adam optimizer를 사용
- At inference time, we run the generator net in exactly the same manner as during the training phase. This differs from the usual protocol in that we apply dropout at test time, and we apply batch normalization using the statistics of the test batch, rather than aggregated statistics of the training batch. This approach to batch normalization, when the batch size is set to 1, has been termed “instance normalization” and has been demonstrated to be effective at image generation tasks. In our experiments, we use batch sizes between 1 and 10 depending on the experiment.
- 자세한 내용은 논문 참고
4. Experiments
4.1 Analysis of the objection function
L1만을 사용하면 진짜같지만 blurry 현상이 심하고, cGAN만을 사용하면 이미지가 선명해지지만 현실성이 떨어진다. 이 둘을 같이 사용한 이미지의 완성도가 가장 높았다.
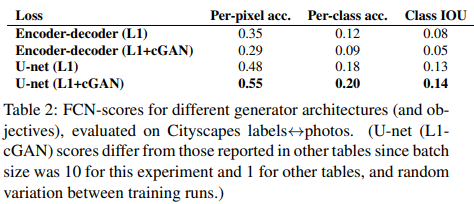
4.2 Analysis of the Generator architecture
U-net을 사용했을 때가 Encoder-Decoder를 사용했을 때 보다 이미지가 잘 생성된다. (FCN-score가 더 높음)
- skip connection을 통해 Encoder의 high-resolution을 decoder에 잘 전달
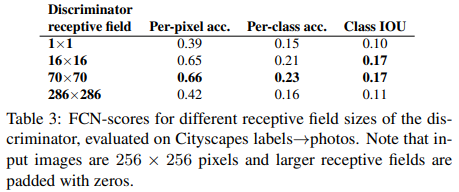
4.3 Analysis of the Discriminator architecture
70 x 70 PatchGAN을 사용했을 때 가장 좋은 FCN-score를 얻었다.
5. Conclusion
Pix2Pix 는 image-to-image translation에 convolutional GAN의 network를 적용하여 좋은 성과를 낸 모델로, 많은 image-to-image의 baseline이 되고있다.
6. Images
Reference
- Naver AI LAB 최윤제 연구원님 발표자료









댓글남기기